

District Disability Rehabilitation Centre, Ahilyanagar
( Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment, Govt. of India approved)
जिल्हा दिव्यांग पुनर्वसन केंद्र, अहिल्यानगर
( सामाजिक न्याय व अधिकारिता मंत्रालय भारत सरकार द्वारा नियुक्त )






District Disability Rehabilitation Centre, Ahilyanagar
जिल्हा दिव्यांग पुनर्वसन केंद्र, अहिल्यानगर
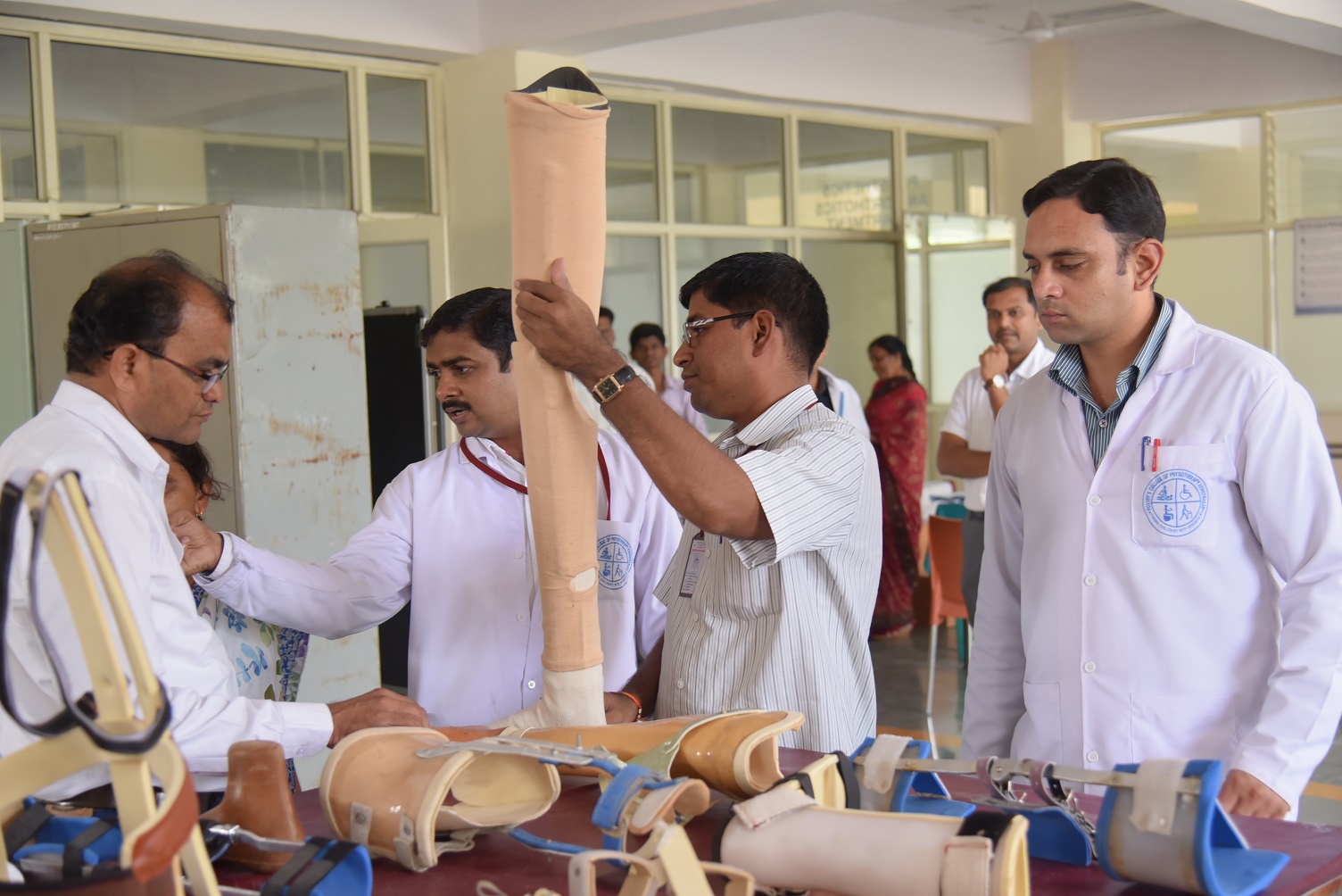










Join Our Mission to Improve a Feature of persons with disabilities.